Develop
Making Test for devices with upydev/upydevice + pytest
Simple tests definitions
Using upydevice/test/ as a template is easy to create custom tests for a device, to be run interactively, which can range from entire modules to single functions, e.g.
Note
pytest and pytest-benchmark required. Install with
$ pip install pytest pytest-benchmark
Consider test test_blink_led from test_esp_serial.py
This will test led on() and off() functions:
def test_blink_led():
TEST_NAME = 'BLINK LED'
if dev.dev_platform == 'esp8266':
_ESP_LED = 2
elif dev.dev_platform == 'esp32':
_ESP_LED = 13
_led = dev.cmd("'led' in globals()", silent=True, rtn_resp=True) # define led if not already defined
if not _led:
dev.cmd('from machine import Pin; led = Pin({}, Pin.OUT)'.format(_ESP_LED))
for i in range(2):
dev.cmd('led.on();print("LED: ON")')
time.sleep(0.2)
dev.cmd('led.off();print("LED: OFF")')
time.sleep(0.2)
try:
assert dev.cmd('not led.value()', silent=True,
rtn_resp=True), 'LED is on, should be off'
do_pass(TEST_NAME)
print('Test Result: ', end='')
except Exception as e:
do_fail(TEST_NAME)
print('Test Result: ', end='')
raise e
or testing a module test_code.py in device that will test upylog.py logging functions.
Consider test test_run_script from test_esp_serial.py
def test_run_script(): # the name of the test for pytest
TEST_NAME = 'RUN SCRIPT' # the name of the test to display in log
log.info('{} TEST: test_code.py'.format(TEST_NAME))
dev.wr_cmd('import test_code', follow=True)
try:
assert dev.cmd('test_code.RESULT', silent=True,
rtn_resp=True) is True, 'Script did NOT RUN'
dev.cmd("import sys,gc;del(sys.modules['test_code']);gc.collect()") # reloads module
do_pass(TEST_NAME)
print('Test Result: ', end='')
except Exception as e:
do_fail(TEST_NAME)
print('Test Result: ', end='')
raise e
So running this test
test $ upydev pytest test_esp_serial.py
Running pytest with Device: sdev
=========================================== test session starts ===========================================
platform darwin -- Python 3.7.9, pytest-7.1.2, pluggy-1.0.0
benchmark: 3.4.1 (defaults: timer=time.perf_counter disable_gc=False min_rounds=5 min_time=0.000005 max_time=1.0 calibration_precision=10 warmup=False warmup_iterations=100000)
rootdir: /Users/carlosgilgonzalez/Desktop/MY_PROJECTS/MICROPYTHON/TOOLS/upydevice_.nosync/test, configfile: pytest.ini
plugins: benchmark-3.4.1
collected 7 items
test_esp_serial.py::test_devname PASSED
test_esp_serial.py::test_platform
---------------------------------------------- live log call ----------------------------------------------
20:09:36 [pytest] [sdev] [ESP32] : Running SerialDevice test...
20:09:36 [pytest] [sdev] [ESP32] : DEV PLATFORM: esp32
SerialDevice @ /dev/cu.usbserial-016418E3, Type: esp32, Class: SerialDevice
Firmware: MicroPython v1.19.1-285-gc4e3ed964-dirty on 2022-08-12; ESP32 module with ESP32
CP2104 USB to UART Bridge Controller, Manufacturer: Silicon Labs
(MAC: 30:ae:a4:23:35:64)
20:09:37 [pytest] [sdev] [ESP32] : DEV PLATFORM TEST: [✔]
Test Result: PASSED
test_esp_serial.py::test_blink_led LED: ON
LED: OFF
LED: ON
LED: OFF
---------------------------------------------- live log call ----------------------------------------------
20:09:39 [pytest] [sdev] [ESP32] : BLINK LED TEST: [✔]
Test Result: PASSED
test_esp_serial.py::test_run_script
---------------------------------------------- live log call ----------------------------------------------
20:09:39 [pytest] [sdev] [ESP32] : RUN SCRIPT TEST: test_code.py
2022-08-17 19:09:38 [log_test] [INFO] Test message2: 100(foobar)
2022-08-17 19:09:38 [log_test] [WARN] Test message3: %d(%s)
2022-08-17 19:09:38 [log_test] [ERROR] Test message4
2022-08-17 19:09:38 [log_test] [CRIT] Test message5
2022-08-17 19:09:38 [None] [INFO] Test message6
2022-08-17 19:09:38 [log_test] [ERROR] Exception Ocurred
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "test_code.py", line 14, in <module>
ZeroDivisionError: divide by zero
2022-08-17 19:09:38 [errorlog_test] [ERROR] Exception Ocurred
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "test_code.py", line 20, in <module>
ZeroDivisionError: divide by zero
20:09:40 [pytest] [sdev] [ESP32] : RUN SCRIPT TEST: [✔]
Test Result: PASSED
test_esp_serial.py::test_raise_device_exception
---------------------------------------------- live log call ----------------------------------------------
20:09:40 [pytest] [sdev] [ESP32] : DEVICE EXCEPTION TEST: b = 1/0
[DeviceError]:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ZeroDivisionError: divide by zero
20:09:40 [pytest] [sdev] [ESP32] : DEVICE EXCEPTION TEST: [✔]
Test Result: PASSED
test_esp_serial.py::test_reset
---------------------------------------------- live log call ----------------------------------------------
20:09:40 [pytest] [sdev] [ESP32] : DEVICE RESET TEST
Rebooting device...
Done!
20:09:41 [pytest] [sdev] [ESP32] : DEVICE RESET TEST: [✔]
Test Result: PASSED
test_esp_serial.py::test_disconnect
---------------------------------------------- live log call ----------------------------------------------
20:09:41 [pytest] [sdev] [ESP32] : DEVICE DISCONNECT TEST
20:09:41 [pytest] [sdev] [ESP32] : DEVICE DISCONNECT TEST: [✔]
Test Result: PASSED
============================================ 7 passed in 5.08s ============================================
Advanced tests definitions using yaml files
It is possible to use parametric test generation using yaml files e.g.
consider test_dev.py in upydev/tests.
Defining a test in a yaml file with the following directives:
Test Directives
name: The name of the test
hint: Info about the test, description, context, etc.
reset: To reset the device (
softorhard) before running the test.load: To load and execute a local file in device (.e.g
test_basic_math.py)command: The command to run the test in device.
args: To pass argument to the test function in device.
kwargs: To pass keyword arguments to the test function in device.
result: The command to get test result.
exp: Expected result to assert.
exp_type: Expected type of result to assert.
assert_op: Assert operation if other than
==.assert_itr: Assert elements of iterable result (
any, orall).benchmark: To run a benchmark of the function (device time). (
pytest-benchmarkplugin required)bench_host: To capture benchmark time of device + host (total time)
diff: To compute diff between device and host benchmark times (i.e. interface latency)
follow: To follow device benchmark output only (host+device time).
rounds: Rounds to run the function if doing a benchmark.
unit: To specify units if the measure is other than time in seconds. (i.e sensors)
network: To run network tests, (currently only
iperf3:server,iperf3:client)ip: IP to use in network tests, (
localip, ordevip)reload: To reload a script in device so it can be run again .e.g reload
foo_testmodule if command wasimport foo_test.
Note
load can be a command too, .e.g import mytestlib although it won’t return anything (only stdout).
Tip
Some directives are mutually exclusive, e.g. the 3 types of tests would be:
Assert Test: using command, result, exp (with options like exp_type, assert_op, assert_itr)
Benchmark Test: using benchmark with rounds and options like bench_host, diff, follow, unit…
Network Test: using network, command, ip to run network tests.
The directives that should work with any type of test are the rest ( name, load, args, kwargs, hint, reload, reset )
---
- name: "sum"
load: ./dev_tests/test_basic_math.py
command: "a = do_sum"
args: [1, 1]
result: a
exp: 2
- name: "diff"
command: "a = do_diff"
args: [1, 1]
result: a
exp: 0
- name: "product"
command: "a = do_product"
args: [2, 2]
result: a
exp: 4
- name: "division"
command: "a = do_div"
args: [1, 2]
result: a
exp: 0.5
def do_sum(a, b):
return a + b
def do_diff(a, b):
return a - b
def do_div(a, b):
return a / b
def do_product(a, b):
return a * b
tests $ upydev pytest test_load_basic_math.yaml
Running pytest with Device: pybV1.1
===================================================== test session starts =====================================================
platform darwin -- Python 3.7.9, pytest-7.1.2, pluggy-1.0.0
benchmark: 3.4.1 (defaults: timer=time.perf_counter disable_gc=False min_rounds=5 min_time=0.000005 max_time=1.0 calibration_precision=10 warmup=False warmup_iterations=100000)
rootdir: /Users/carlosgilgonzalez/Desktop/MY_PROJECTS/MICROPYTHON/TOOLS/upydev_.nosync/tests, configfile: pytest.ini
plugins: benchmark-3.4.1
collected 7 items
test_dev.py::test_devname PASSED
test_dev.py::test_platform
-------------------------------------------------------- live log call --------------------------------------------------------
17:06:44 [pytest] [pybV1.1] [PYBOARD] : Running SerialDevice test...
17:06:44 [pytest] [pybV1.1] [PYBOARD] : DEV PLATFORM: pyboard
17:06:44 [pytest] [pybV1.1] [PYBOARD] : DEV PLATFORM TEST: [✔]
Test Result: PASSED
test_dev.py::test_dev[sum]
-------------------------------------------------------- live log call --------------------------------------------------------
17:06:44 [pytest] [pybV1.1] [PYBOARD] : Running [sum] test...
17:06:44 [pytest] [pybV1.1] [PYBOARD] : Loading ./dev_tests/test_basic_math.py file...
17:06:44 [pytest] [pybV1.1] [PYBOARD] : Command [a = do_sum(*[1, 1])]
17:06:45 [pytest] [pybV1.1] [PYBOARD] : expected: 2 --> result: 2
17:06:45 [pytest] [pybV1.1] [PYBOARD] : sum TEST: [✔]
Test Result: PASSED
test_dev.py::test_dev[diff]
-------------------------------------------------------- live log call --------------------------------------------------------
17:06:45 [pytest] [pybV1.1] [PYBOARD] : Running [diff] test...
17:06:45 [pytest] [pybV1.1] [PYBOARD] : Command [a = do_diff(*[1, 1])]
17:06:45 [pytest] [pybV1.1] [PYBOARD] : expected: 0 --> result: 0
17:06:45 [pytest] [pybV1.1] [PYBOARD] : diff TEST: [✔]
Test Result: PASSED
test_dev.py::test_dev[product]
-------------------------------------------------------- live log call --------------------------------------------------------
17:06:45 [pytest] [pybV1.1] [PYBOARD] : Running [product] test...
17:06:45 [pytest] [pybV1.1] [PYBOARD] : Command [a = do_product(*[2, 2])]
17:06:45 [pytest] [pybV1.1] [PYBOARD] : expected: 4 --> result: 4
17:06:45 [pytest] [pybV1.1] [PYBOARD] : product TEST: [✔]
Test Result: PASSED
test_dev.py::test_dev[division]
-------------------------------------------------------- live log call --------------------------------------------------------
17:06:45 [pytest] [pybV1.1] [PYBOARD] : Running [division] test...
17:06:45 [pytest] [pybV1.1] [PYBOARD] : Command [a = do_div(*[1, 2])]
17:06:45 [pytest] [pybV1.1] [PYBOARD] : expected: 0.5 --> result: 0.5
17:06:45 [pytest] [pybV1.1] [PYBOARD] : division TEST: [✔]
Test Result: PASSED
test_dev.py::test_disconnect
-------------------------------------------------------- live log call --------------------------------------------------------
17:06:45 [pytest] [pybV1.1] [PYBOARD] : DEVICE DISCONNECT TEST
17:06:45 [pytest] [pybV1.1] [PYBOARD] : DEVICE DISCONNECT TEST: [✔]
Test Result: PASSED
====================================================== 7 passed in 1.76s ======================================================
Note
pytest command will by default use test_dev.py if only yaml files indicated
Running Benchmarks with pytes-benchmark
See pytest-benchmark documentation
To write a benchmark test use benchmark directive to indicate a function that will be called rounds times (default 5). Consider this example:
---
- name: System Check
hint: "Device CPU frequency:"
command: "import machine;machine.freq()"
- name: Pystone Benchmark
hint: Run 500 loops, returns time in seconds to complete a run.
load: "import pystone_lowmem"
benchmark: "pystone_lowmem.main"
args: [500, True]
reload: "pystone_lowmem"
Where the function pystone_lowmem.main(500,True) will perform a 500 loops run and
return the time that it took in seconds.
Tip
Use of time.ticks_ms/time.ticks_us and time.ticks_diff to obtain the
time that it takes to run any function and return time in seconds e.g.
def benchmark_this(func, *args, **kwargs):
t0 = time.ticks_ms()
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
delta = time.ticks_diff(time.ticks_ms(), t0)
return delta/1e3 # delta/1e6 if using time.ticks_us
Running test_benchmark/test_pystone_bmk.yaml benchmark with different devices
and saving benchmark results
$ pyb pytest test_benchmark/test_pystones_bmk.yaml --benchmark-save=pyb_pystones
...
$ gk32 pytest test_benchmark/test_pystones_bmk.yaml --benchmark-save=gk32_pystones
...
$ sdev pytest test_benchmark/test_pystones_bmk.yaml --benchmark-save=sdev_pystones
...
$ oble pytest test_benchmark/test_pystones_bmk.yaml --benchmark-save=oble_pystones
...
It is possible to compare benchmark results e.g.
$ pytest-benchmark compare "*pystone*"
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- benchmark 'device': 4 tests ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Name (time in ms) Min Max Mean StdDev Median IQR Outliers OPS Rounds Iterations
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
test_dev[Pystone Benchmark]:[gkesp32@esp32] (0002_gk32_py) 188.0000 (1.0) 197.0000 (1.0) 192.8000 (1.0) 4.0249 (4.50) 195.0000 (1.0) 6.7500 (5.40) 2;0 5.1867 (1.0) 5 1
test_dev[Pystone Benchmark]:[pybV1.1@pyboard] (0001_pyb_pys) 262.0000 (1.39) 264.0000 (1.34) 263.4000 (1.37) 0.8944 (1.0) 264.0000 (1.35) 1.2500 (1.0) 1;0 3.7965 (0.73) 5 1
test_dev[Pystone Benchmark]:[oble@esp32] (0003_oble_py) 264.0000 (1.40) 267.0000 (1.36) 265.2000 (1.38) 1.3038 (1.46) 265.0000 (1.36) 2.2500 (1.80) 1;0 3.7707 (0.73) 5 1
test_dev[Pystone Benchmark]:[sdev@esp32] (0004_sdev_py) 282.0000 (1.50) 292.0000 (1.48) 288.4000 (1.50) 3.9115 (4.37) 289.0000 (1.48) 4.7500 (3.80) 1;0 3.4674 (0.67) 5 1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Legend:
Outliers: 1 Standard Deviation from Mean; 1.5 IQR (InterQuartile Range) from 1st Quartile and 3rd Quartile.
OPS: Operations Per Second, computed as 1 / Mean
To see device firmware use --group-by=param
$ pytest-benchmark compare "*pystone*" --group-by=param
---------- benchmark 'Pystone Benchmark @ esp32 micropython-v1.18-128-g2ea21abae-dirty on 2022-02-19 4MB/OTA BLE module with ESP32': 1 tests -----------
Name (time in ms) Min Max Mean StdDev Median IQR Outliers OPS Rounds Iterations
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
test_dev[Pystone Benchmark]:[oble@esp32] (0003_oble_py) 264.0000 267.0000 265.2000 1.3038 265.0000 2.2500 1;0 3.7707 5 1
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------ benchmark 'Pystone Benchmark @ esp32 micropython-v1.19.1-304-g5b7abc757-dirty on 2022-08-23 ESP32 module with ESP32': 1 tests -------------
Name (time in ms) Min Max Mean StdDev Median IQR Outliers OPS Rounds Iterations
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
test_dev[Pystone Benchmark]:[sdev@esp32] (0004_sdev_py) 282.0000 292.0000 288.4000 3.9115 289.0000 4.7500 1;0 3.4674 5 1
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-------------- benchmark 'Pystone Benchmark @ esp32 micropython-v1.19.1-321-gb9b5404bb on 2022-08-24 4MB/OTA SSL module with ESP32': 1 tests --------------
Name (time in ms) Min Max Mean StdDev Median IQR Outliers OPS Rounds Iterations
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
test_dev[Pystone Benchmark]:[gkesp32@esp32] (0002_gk32_py) 188.0000 197.0000 192.8000 4.0249 195.0000 6.7500 2;0 5.1867 5 1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
----------------- benchmark 'Pystone Benchmark @ pyboard micropython-v1.19.1-217-g5234e1f1e on 2022-07-29 PYBv1.1 with STM32F405RG': 1 tests ----------------
Name (time in ms) Min Max Mean StdDev Median IQR Outliers OPS Rounds Iterations
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
test_dev[Pystone Benchmark]:[pybV1.1@pyboard] (0001_pyb_pys) 262.0000 264.0000 263.4000 0.8944 264.0000 1.2500 1;0 3.7965 5 1
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Legend:
Outliers: 1 Standard Deviation from Mean; 1.5 IQR (InterQuartile Range) from 1st Quartile and 3rd Quartile.
OPS: Operations Per Second, computed as 1 / Mean
To see the command/hint/context of the benchmark use --group-by=param:cmd
$ pytest-benchmark compare "*pys*" --group-by=param:cmd
benchmark "cmd={'name': 'Pystone Benchmark', 'hint': 'Run 500 loops, returns time in seconds to complete a run.', 'load': 'import pystone_lowmem', 'benchmark': 'pystone_lowmem.main(benchtm=True)', 'reload': 'pystone_lowmem'}": 4 tests
Name (time in ms) Min Max Mean StdDev Median IQR Outliers OPS Rounds Iterations
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
test_dev[Pystone Benchmark]:[gkesp32@esp32] (0002_gk32_py) 188.0000 (1.0) 197.0000 (1.0) 192.8000 (1.0) 4.0249 (4.50) 195.0000 (1.0) 6.7500 (5.40) 2;0 5.1867 (1.0) 5 1
test_dev[Pystone Benchmark]:[pybV1.1@pyboard] (0001_pyb_pys) 262.0000 (1.39) 264.0000 (1.34) 263.4000 (1.37) 0.8944 (1.0) 264.0000 (1.35) 1.2500 (1.0) 1;0 3.7965 (0.73) 5 1
test_dev[Pystone Benchmark]:[oble@esp32] (0003_oble_py) 264.0000 (1.40) 267.0000 (1.36) 265.2000 (1.38) 1.3038 (1.46) 265.0000 (1.36) 2.2500 (1.80) 1;0 3.7707 (0.73) 5 1
test_dev[Pystone Benchmark]:[sdev@esp32] (0004_sdev_py) 282.0000 (1.50) 292.0000 (1.48) 288.4000 (1.50) 3.9115 (4.37) 289.0000 (1.48) 4.7500 (3.80) 1;0 3.4674 (0.67) 5 1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Legend:
Outliers: 1 Standard Deviation from Mean; 1.5 IQR (InterQuartile Range) from 1st Quartile and 3rd Quartile.
OPS: Operations Per Second, computed as 1 / Mean
It is possible to benchmark measurements other than time, i.e. to benchmark sensor measurements.
Use unit directive in yaml file to indicate the unit or measurement and unit, e.g.
unit: "V" or unit: "voltage:V". This also can be set at the command line with
--unit option.
Let’s consider this example to take measurements with an ADC sensor ADS1115
---
- name: i2c_config
load: "from machine import I2C, Pin"
command: "i2c=I2C"
args: "[1]"
kwargs: "{'scl': Pin(22), 'sda': Pin(23)}"
- name: i2c_scan
command: "addr=i2c.scan()"
result: "i2c.scan()"
exp: [72]
exp_type: list
- name: ads_config
command: "from ads1115 import ADS1115;sensor=ADS1115(i2c,
addr[0], 1); sensor.set_conv(7, channel1=0)"
- name: ads_read
command: "mv = sensor.raw_to_v(sensor.read())"
result: mv
exp: 0
assert_op: "<="
exp_type: float
- name: ADS1115 Benchmark
hint: Test ADS1115 ADC sensor
load: "import time"
benchmark: "[(time.time_ns(), sensor.raw_to_v(sensor.read())) for i in range(100)]"
unit: "voltage:V"
rounds: 1
$ espd pytest test_ads/test_ads_bmk.yaml --benchmark-save=espd_ads1115 --benchmark-save-data
Running pytest with Device: espdev
Comparing against benchmarks from: Darwin-CPython-3.7-64bit/0022_espd_ads1115.json
===================================================================================================================== test session starts =====================================================================================================================
platform darwin -- Python 3.7.9, pytest-7.1.2, pluggy-1.0.0
benchmark: 3.4.1 (defaults: timer=time.perf_counter disable_gc=False min_rounds=5 min_time=0.000005 max_time=1.0 calibration_precision=10 warmup=False warmup_iterations=100000)
rootdir: /Users/carlosgilgonzalez/Desktop/MY_PROJECTS/MICROPYTHON/TOOLS/upydev_.nosync/tests, configfile: pytest.ini
plugins: benchmark-3.4.1
collected 8 items
test_dev.py::test_devname PASSED
test_dev.py::test_platform
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ live log call ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
23:35:13 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : Running WebSocketDevice test...
23:35:13 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : Device: esp32
23:35:13 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : Firmware: micropython v1.19.1-304-g5b7abc757-dirty on 2022-08-23; ESP32 module with ESP32
23:35:13 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : DEV PLATFORM TEST: [✔]
Test Result: PASSED
test_dev.py::test_dev[i2c_config]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ live log call ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
23:35:13 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : Running [i2c_config] test...
23:35:13 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : Loading from machi... snippet
paste mode; Ctrl-C to cancel, Ctrl-D to finish
=== from machine import I2C, Pin
23:35:14 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : Command [i2c=I2C(*[1], **{'scl': Pin(22), 'sda': Pin(23)})]
23:35:14 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : i2c_config TEST: [✔]
Test Result: PASSED
test_dev.py::test_dev[i2c_scan]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ live log call ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
23:35:14 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : Running [i2c_scan] test...
23:35:14 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : Command [addr=i2c.scan()]
23:35:15 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : expected: list --> result: <class 'list'>
23:35:15 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : expected: [72] == result: [72]
23:35:15 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : i2c_scan TEST: [✔]
Test Result: PASSED
test_dev.py::test_dev[ads_config]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ live log call ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
23:35:15 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : Running [ads_config] test...
23:35:15 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : Command [from ads1115 import ADS1115;sensor=ADS1115(i2c, addr[0], 1); sensor.set_conv(7, channel1=0)]
23:35:16 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : ads_config TEST: [✔]
Test Result: PASSED
test_dev.py::test_dev[ads_read]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ live log call ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
23:35:16 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : Running [ads_read] test...
23:35:16 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : Command [mv = sensor.raw_to_v(sensor.read())]
23:35:17 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : expected: float --> result: <class 'float'>
23:35:17 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : expected: 0 <= result: 0.5788927
23:35:17 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : ads_read TEST: [✔]
Test Result: PASSED
test_dev.py::test_dev[ADS1115 Benchmark]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ live log call ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
23:35:17 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : Running [ADS1115 Benchmark] test...
23:35:17 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : Loading import tim... snippet
paste mode; Ctrl-C to cancel, Ctrl-D to finish
=== import time
23:35:18 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : Hint: Test ADS1115 ADC sensor
23:35:18 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : Benchmark Command [[(time.time_ns(), sensor.raw_to_v(sensor.read())) for i in range(100)]]
[(715559717849154000, 0.5791427), (715559717862555000, 0.5806427), (715559717872601000, 0.5815177), (715559717882546000, 0.5813928), (715559717892413000, 0.5820178), (715559717902349000, 0.5815177), (715559717912478000, 0.5811427), (715559717922413000, 0.5811427), (715559717932291000, 0.5812678), (715559717942212000, 0.5816427), (715559717952415000, 0.5815177), (715559717962345000, 0.5813928), (715559717972224000, 0.5813928), (715559717982118000, 0.5810177), (715559717992065000, 0.5815177), (715559718002000000, 0.5812678), (715559718011880000, 0.5811427), (715559718021805000, 0.5816427), (715559718031787000, 0.5808928), (715559718041728000, 0.5811427), (715559718051652000, 0.5815177), (715559718061669000, 0.5813928), (715559718071616000, 0.5813928), (715559718081553000, 0.5811427), (715559718091440000, 0.5811427), (715559718101334000, 0.5813928), (715559718111284000, 0.5813928), (715559718121221000, 0.5811427), (715559718131099000, 0.5808928), (715559718140997000, 0.5808928), (715559718150945000, 0.5811427), (715559718160970000, 0.5813928), (715559718170853000, 0.5817678), (715559718180773000, 0.5810177), (715559718190747000, 0.5808928), (715559718200688000, 0.5813928), (715559718210567000, 0.5807677), (715559718220463000, 0.5817678), (715559718230410000, 0.5805177), (715559718240350000, 0.5808928), (715559718250236000, 0.5810177), (715559718260293000, 0.5808928), (715559718270243000, 0.5811427), (715559718280178000, 0.5811427), (715559718290054000, 0.5811427), (715559718299951000, 0.5808928), (715559718309908000, 0.5805177), (715559718319844000, 0.5811427), (715559718329721000, 0.5806427), (715559718339619000, 0.5812678), (715559718349568000, 0.5813928), (715559718359641000, 0.5813928), (715559718370132000, 0.5813928), (715559718380101000, 0.5810177), (715559718390056000, 0.5807677), (715559718399996000, 0.5813928), (715559718409886000, 0.5810177), (715559718419775000, 0.5810177), (715559718429732000, 0.5816427), (715559718439670000, 0.5811427), (715559718449554000, 0.5808928), (715559718459455000, 0.5813928), (715559718469707000, 0.5811427), (715559718479695000, 0.5811427), (715559718489586000, 0.5815177), (715559718499520000, 0.5812678), (715559718509505000, 0.5805177), (715559718519437000, 0.5813928), (715559718529372000, 0.5808928), (715559718539332000, 0.5808928), (715559718549288000, 0.5811427), (715559718559336000, 0.5810177), (715559718569478000, 0.5807677), (715559718579373000, 0.5813928), (715559718589322000, 0.5810177), (715559718599262000, 0.5812678), (715559718609149000, 0.5806427), (715559718619041000, 0.5816427), (715559718628992000, 0.5812678), (715559718638925000, 0.5812678), (715559718648820000, 0.5812678), (715559718658717000, 0.5818928), (715559718668752000, 0.5808928), (715559718678688000, 0.5808928), (715559718688632000, 0.5807677), (715559718698531000, 0.5813928), (715559718708483000, 0.5808928), (715559718718414000, 0.5816427), (715559718728302000, 0.5808928), (715559718738192000, 0.5806427), (715559718748135000, 0.5812678), (715559718758075000, 0.5813928), (715559718768006000, 0.5807677), (715559718778015000, 0.5808928), (715559718787963000, 0.5816427), (715559718797895000, 0.5811427), (715559718807782000, 0.5812678), (715559718817676000, 0.5811427), (715559718827620000, 0.5808928), (715559718837561000, 0.5808928)]
23:35:20 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : ADS1115 Benchmark TEST: [✔]
Test Result: PASSED
test_dev.py::test_disconnect
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ live log call ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
23:35:20 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : DEVICE DISCONNECT TEST
23:35:20 [pytest] [espdev] [ESP32] : DEVICE DISCONNECT TEST: [✔]
Test Result: PASSED
Saved benchmark data in: /Users/carlosgilgonzalez/Desktop/MY_PROJECTS/MICROPYTHON/TOOLS/upydev_.nosync/tests/.benchmarks/Darwin-CPython-3.7-64bit/0023_espd_ads1115.json
------------------------------------------------------- benchmark 'device': 1 tests -------------------------------------------------------
Name (voltage in mV) Min Max Mean StdDev Median IQR Outliers OPS Rounds Iterations
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
test_dev[ADS1115 Benchmark]:[espdev@esp32] 579.1427 582.0178 581.1515 0.3732 581.1427 0.5000 23;1 1.7207 100 1
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Legend:
Outliers: 1 Standard Deviation from Mean; 1.5 IQR (InterQuartile Range) from 1st Quartile and 3rd Quartile.
OPS: Operations Per Second, computed as 1 / Mean
===================================================================================================================== 8 passed in 13.40s ======================================================================================================================
Tip
benchmark directive accepts single value, a list of values or a list of 2 values tuples, where the first value is a time value and the second is the measurement to benchmark.
Note
To save benchmark results (i.e not only the stats) use --benchmark-save=[NAME] --benchmark-save-data
Data will be saved in .benchmarks/[SYSTEM PLATFORM]/xxxx_[NAME].json, e.g.
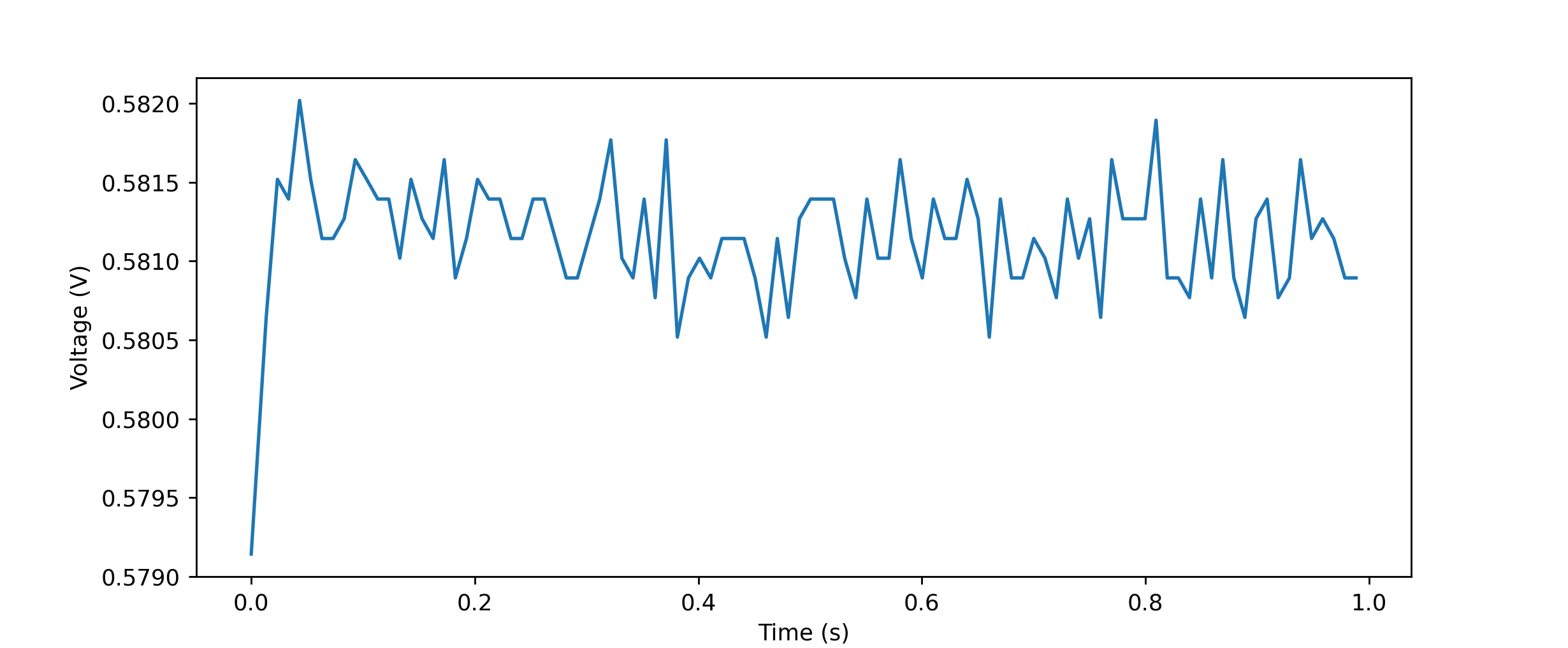
import json
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import sys
file = sys.argv[1]
with open(file, 'r') as rp:
report = json.load(rp)
data = report['benchmarks'][0]['stats']['data']
time_stamp = report['benchmarks'][0]['extra_info']['vtime']
# from absolute timestamps in ns to relative time in seconds
t_vec = [(t-time_stamp[0])/1e9 for t in time_stamp]
plt.plot(t_vec, data)
plt.ylabel("Voltage ($V$)")
plt.xlabel("Time ($s$)")
plt.show()
$ ./plot.py .benchmarks/Darwin-CPython-3.7-64bit/0023_espd_ads1115.json
Vim Integration
Here are some keybindings and commands to make it easier work with vim + upydev that can be added to ~/.vimrc.
These commands and keybindings make it pretty easy to iterate and run/upload current file or blocks of code in device.
upload file to device
To upload current file to a device add this to ~/.vimrc
" Terminal
set shell=bash\ -l " make it use bash with ~/.profile or ~/.bash_rc
" UPYDEV
" Upload current file to device
command U !upydev put %:.
" Upl <device> :Upload current file to <device>
command! -nargs=1 Upl !upydev put %:. -@ <q-args>
" Keybinding to upload current file to device
noremap <C-i> :U<CR><CR>
" Upload current file to device using an open terminal shell-repl
command PutOnTerm :call term_list()[0]->term_sendkeys("put " .. expand('%:.') .."\<CR>")
nnoremap <leader>u :PutOnTerm <CR><CR>
shell-repl
To open shell-repl in a terminal window inside vim:
" Open terminal at bottom and open shell-repl
command Shl :bo term++rows=15 ++close upydev shl
" Open terminal at bottom and open jupyter console with upydevice kernel
command Jpy :bo term++rows=15 ++close upydev jupyterc
" Command to run upydev pytest with current file
command Upyt !upydev pytest %:.
" Keybinding to run Upyt command
nnoremap <Leader>t :Upyt <CR>
" Command to show upydev global group
command SG :bo term++rows=15 upydev gg
" Sh <device> command to open a termial at the bottom with shell-repl @ <device>
command! -nargs=1 Sh :bo term++rows=15 ++close upydev shl -@ <q-args>
"St <device> :Set upydev global device config.
command! -nargs=1 St !upydev set -g -@ <q-args>
run current file
Run current file or lines of code in device
" Keybinding to execute current file in device
nnoremap <C-f> :!upydev load <C-r>=expand('%:.')<cr> <CR>
" Execute current line on an open terminal REPL
command ExecOnTerm :call term_list()[0]->term_sendkeys(getline('.') .. "\<CR>")
nnoremap <leader>e :ExecOnTerm <CR><CR>
" Execute current file on an open terminal shell-rep
command LoadOnTerm :call term_list()[0]->term_sendkeys("load " .. expand('%:.') .."\<CR>")
nnoremap <leader>l :LoadOnTerm <CR><CR>
" Execute current line selection in an open terminal REPL
command ExecBuffOnTerm :call term_list()[0]->term_sendkeys(join(getline(1,'$'), "\<cr>").."\<CR>")
nnoremap <leader>r :ExecBuffOnTerm <CR><CR>
run test files
Run current test file with upydev + pytest
" Run current test file with upydev + pytest
command Upyt !upydev pytest %:.
nnoremap <Leader>T :Upyt<CR>
" "" in terminal window below
command Upytb :bo term++rows=15 upydev pytest %:.
nnoremap <leader>t :Upytb <CR>
" Run pytest of current file using an open terminal shell-repl
command TestOnTerm :call term_list()[0]->term_sendkeys("pytest " .. expand('%:.') .."\<CR>")
nnoremap <leader>y :TestOnTerm <CR><CR>
MicroPython (Unix)
Here are some commands/keybindings to integrate MicroPython (unix)
" MICROPYTHON
" Command to run current file in MicroPython
command Mr !micropython %:.
" Same as before but stay at the REPL after executing the file.
command Mi !micropython -i %:.
" Open a terminal MicroPython REPL at the bottom
command Upy :bo term++rows=15 ++close micropython
MicroPython stubs for code autocompletion
Micropython stubs:
Stubs that enable code autocompletion of MicroPython modules. See micropython-stubs.
YouCompleteMe:
plugin for vim autocompletion see ycm and Python Semantic completion
e.g add
.ycm_extra_conf.pyto your project dirdef Settings(**kwargs): return { "sys_path": [ ( "/<path-to>/micropython-stubs/stubs/micropython-v1_19_1-esp32" ) ] }
and this
let g:ycm_extra_conf_globlist=['./*']to~/.vimrc
Git Integration
Use git to track your device project and push changes to your device as it were a remote git repository.
Init your project dir as a git repo
$ git init .
Create a dir inside your project directory
$ mkdir <device>.git
Init remote device “bare” repo
$ cd <device>.git
and
$ git --bare init
Make device repo work as a server
$ git --bare update-server-info
and
$ mv hooks/post-update.sample hooks/post-update
Now go back to project dir, enable git pre-push hook to call upydev dsync and
push changes to device.
$ cd ..
$ vim .git/hooks/pre-push
This hook checks that if remote repo that is been pushed is <device> (gk32 in this example)
and calls upydev dsync to push commit changes to device.
#!/bin/sh
# An example hook script to verify what is about to be pushed. Called by "git
# push" after it has checked the remote status, but before anything has been
# pushed. If this script exits with a non-zero status nothing will be pushed.
#
# This hook is called with the following parameters:
#
# $1 -- Name of the remote to which the push is being done
# $2 -- URL to which the push is being done
#
# If pushing without using a named remote those arguments will be equal.
#
# Information about the commits which are being pushed is supplied as lines to
# the standard input in the form:
#
# <local ref> <local oid> <remote ref> <remote oid>
#
# This sample shows how to prevent push of commits where the log message starts
# with "WIP" (work in progress).
remote=$1
if test $remote = "gk32" # change to match device remote repo
then
device=$(upydev -@ gkesp32) # change to match device name
echo "Pushing to: "
echo $device
upydev dsync "git@main...gk32/main" -i "*.key" "./.git*" "./gk32.git*" "*.swp" "./.*" "*.der" "*.pem" "*config.py" -rf -@ gkesp32
# ^- change to match device_repo/branch
fi
exit 0
Note
Note that gk32 is the remote device repo and -@ gkesp32 is device name.
Also note that -i flag is used to ignore files that will not be uploaded
to device in any case.
Now create .gitignore,
add device dir repo to it, e.g. gk32.git* plus any other unwanted file.
Add now device repo as a remote repo
$ git remote add <device> <device>.git
Check e.g.
$ git remote -v
gk32 gk32.git (fetch)
gk32 gk32.git (push)`
Set upstream
$ git branch -u <device>/main
Check
$ git remote show gk32
+ remote gk32
Fetch URL: gk32.git
Push URL: gk32.git
HEAD branch: main
Remote branch:
main tracked
Local branch configured for 'git pull':
main merges with remote main
Local ref configured for 'git push':
main pushes to main (fast-forwardable)
Make some changes, commit and check
$ git status
On branch main
Your branch is ahead of 'gk32/main' by 1 commit.
(use "git push" to publish your local commits)
nothing to commit, working tree clean
$ git branch -vv --all
* main 766d7fb [gk32/main: ahead 1] Test push
remotes/gk32/main 56a43ba Fix log.exception with custom stream class
And finally push
$ git push gk32
Pushing to:
Device: gkesp32 Address: gkesp32.local, Device Type: WebSocketDevice
dsync: syncing path ./:
dsync: dirs: OK[✔]
dsync: syncing modified files (1):
1. ./dummy.py [0.06 kB]
./dummy.py -> gkesp32:./dummy.py
./dummy.py [0.06 kB]
▏████████████████▏ \ 100 % | 0.06/0.06 kB | 103.67 kB/s | 00:00/00:00 s
dsync: files: OK[✔]
0 new files, 1 file changed, 0 files deleted
Enumerating objects: 5, done.
Counting objects: 100% (5/5), done.
Delta compression using up to 4 threads
Compressing objects: 100% (3/3), done.
Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 317 bytes | 317.00 KiB/s, done.
Total 3 (delta 1), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0
To gk32.git
56a43ba..766d7fb main -> main
Device development setups
SerialDevice
The easiest way to develop is having the device directly connected to the computer by USB. It allows a fast develop/test/fix/deploy cycle. It is also possible to make the device act as a peripheral so in can be integrated and controlled from the computer through a simple script, command line tool (like upydev) or even a GUI app. This is also possible using wireless connections, but this one has the lowest latency and the best performance.
To help with a fast development cycle, there are some tools/short-cuts/keybindings in shell-repl that allows
to load code from file into the device buffer to be executed. This is done using a tmp file _tmp_script.py in cwd.
In shell mode: Pressing
CTRL-twill load the contents of_tmp_script.pyin device buffer and execute it. e.g. the file_tmp_script.pywith content:
import time
for i in range(10):
print(f"hello: {i}")
time.sleep(0.1)
Pressing CTRL-t
esp32@sdev:~ $ Running Buffer...
hello: 0
hello: 1
hello: 2
hello: 3
hello: 4
hello: 5
hello: 6
hello: 7
hello: 8
hello: 9
In repl mode: Pressing
CTRL-ewill create/open file_tmp_script.pyto be modified invim. After saving and exit, the content will be loaded in device buffer. Next, pressingCTRL-dwill execute the buffer orCTRL-cto cancel. e.g.
Pressing CTRL-e, saving and exit, then CTRL-d:
Temp Buffer loaded do CTRL-D to execute or CTRL-C to cancel
>>> Running Buffer...
hello: 0
hello: 1
hello: 2
hello: 3
hello: 4
hello: 5
hello: 6
hello: 7
hello: 8
hello: 9
>>>
Using load command in shell mode: This allows to load and execute local scripts in device. This loads a local file content in device buffer and executes it.
esp32@sdev:~ $ load dummy.py
This is a dummy file for testing purpose
Adding custom keybinding to vim to load current file.
Add the following lines to
~/.vimrc
" Execute current file in device
nnoremap <C-f> :!upydev load <C-r>=expand('%:r')<cr>.py <CR>
E.g map CTRL-f to load current file content in device buffer and execute it.
(must save the file first with :w)
Tip
Device buffer is limited so if the file is too big it may be better to upload the file to the device or split the file in smaller ones.
Note
This is also avaible in the shell-repl for WebSocketDevices and BleDevices,
however latency will be higher due to the nature of wireless connections, e.g
higher latency of BleDevices if using a bluetooth headset at the same time.
WebSocketDevice
In upyutils/network there are some modules that may be of help when developing devices that needs to be connected and mantain a reliable connection.
Using wpa_supplicant.py module (check
mpy-wpa_supplicant) allows to the define a configuration file
wpa_supplicant.config with known AP networks ssid:passwords and its function
e.g.
{"my_ssid": "my_pass", "my_ssid2": "my_pass2"}
setup_network() will scan and connect to the closest known AP and return True if
connected.
import wpa_supplicant
if wpa_supplicant.setup_network():
print("Connected")
# Now for example RTC can be set with ntptime.settime()
else:
# Enable device AP instead
print("Enabling AP")
As a bonus to set mDNS host name of the device, add a file named hostname.py with
the name e.g. NAME = "mydevice" and it will be set by wpa_supplicant.setup_network()
too. This allows to use mydevice.local instead of device IP address.
$ ping mydevice.local
PING mydevice.local (192.168.1.53): 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 192.168.1.53: icmp_seq=0 ttl=255 time=100.093 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.1.53: icmp_seq=1 ttl=255 time=21.592 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.1.53: icmp_seq=2 ttl=255 time=239.554 ms
^C
--- mydevice.local ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 packets received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 21.592/120.413/239.554/90.135 ms
In case a device needs to be moved (e.g. is powered by battery or to change device location) A network watchdog can be useful to reset and connect to a new AP or schedule a reconnection attemp.
Module nwatchdog.py defines a Network watchdog class that will init a WatchDog Timer
WDT with a timeout of n+10 and a hardware Timer that will check every n seconds if WLAN is connected,
and feed the WDT if True. Therefore if WLAN is for any reason disconnected the
watchdog will not be fed and it will trigger a reset.
e.g. in combination with wpa_supplicant.py and config module.
from wpa_supplicant import setup_network
from nwatchdog import WatchDog
from watchdog_config import WATCHDOG
from log_config import LOG
import ntptime
import upylog
from hostname import NAME
upylog.basicConfig(level=LOG.level, format='TIME_LVL_MSG')
log = upylog.getLogger(NAME, log_to_file=True, rotate=5000)
if setup_network():
if WATCHDOG.enabled:
wlan = network.WLAN(network.STA_IF)
watch_dog = WatchDog(wlan)
watch_dog.start()
log.info('Network WatchDog started!')
# Set time
try:
ntptime.settime()
except Exception as e:
log.exception(e, "NTP not available")
else:
# set AP
Module ursyslogger.py allows to forward logging messages to a remote host
using rsyslog . Configure rsyslog in remote server
to enable remote logging using TCP, see remote logging with rsyslog.
Then add RsysLogger to log.
...
>>> from ursyslogger import RsysLogger
>>> rsyslog = RsysLogger("server.local", port=514, hostname="mydevice", t_offset="+01:00")
>>> log.remote_logger = rsyslog
>>> log.info("Remote hello")
2022-09-15 10:06:04 [esp32@mydevice] [INFO] Remote hello
Then check in remote server e.g.
$ tail -F mydevice.local.log
Sep 15 10:06:04 mydevice.local esp32@mydevice Remote hello
BleDevice
Once the device is running BleREPL with NUS profile (Nordic UART Service), it is possible
to connect and send commands as with other devices. However due to the nature of
Bluetooth Low Energy, the computer needs to scan first and then connect, which
depending on the advertising period of the device, it may take a bit. This is why connecting
to the device using shell-repl mode is the best way to work. (e.g in case the device cannot
be connected using USB/Serial i.e. no physical access.)
Using config module it is possible to set different operation modes that will switch
between:
Custom ble app/profile (e.g.
Temeperature SensorProfile)Debug Mode, running
BleREPLwithNUSProfile.Bootloader Mode, running
DFUProfile to do OTA firmware updates.
Set mode config with, (in shell-repl)
esp32@oble:~ $ config add mode
esp32@oble:~ $ config mode: app=True blerepl=False dfu=False
mode -> app=True, blerepl=False, dfu=False
and in main.py:
from mode_config import MODE
if MODE.app:
print('App mode')
import myapp
myapp.run()
elif MODE.blerepl:
print('Debug mode')
import ble_uart_repl
ble_uart_repl.start()
elif MODE.dfu:
print('DFU mode')
from otable import BLE_DFU_TARGET
ble_dfu = BLE_DFU_TARGET()
Note
Note that while running in app or dfu mode to switch to another mode, it
should be done by setting mode config using config module and then rebooting the device, using a custom writable characteristic in case of app mode, and in case of dfu mode after a timeout with no connections
or OTA update successfully done (ideally switching to debug / blerepl mode to perform tests. After that
set config to app mode and reboot)